C++学习笔记
C++学习笔记
# C++学习笔记
# 命名空间的using声明
一般用到标准输入输出流的时候,库函数属于命名空间std,用作std::cout、std::cin
或者在开头声明:using namespace std;
或者单独声明:using std::cin;、using std::cout;
# 类型说明符auto
auto:让编译器去分析表达式所属的类型。
auto cnt = 0;
auto pi = 3.14;
# 类型指示符decltype
decltype是declare type的缩写,译为声明类型。
能从表达式的类型推断出变量的类型,如:
decltype(sizeof(arr)) length;
# 基于范围的for语句(range for)
for (declaration : expression)
statement
// 将string中的字符分隔输出
for (auto c : str)
{
cout << c << “ ”;
}
cout << str; // h e l l o w o r l d
// 将string中字符编程大写
// 用上引用符 &
for (auto &c : str)
{
c = toupper(c);
}
cout << str; // HELLO WORLD
# 静态
# 静态成员变量和静态成员函数
类中定义的静态成员、函数,为整个类所有,为所有对象共有,所有对象共享。
可以通过类名访问,也可以通过对象直接访问。
静态成员函数只能直接访问静态变量和静态函数(因为不能实例化)。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class test
{
private:
static int m_value; //定义私有类的静态成员变量
public:
test()
{
m_value++;
}
static int getValue() //定义类的静态成员函数
{
return m_value;
}
};
int test::m_value = 0; //类的静态成员变量需要在类外分配内存空间
int main()
{
test t1;
test t2;
test t3;
cout << "test::m_value2 = " << test::getValue() << endl; //通过类名直接调用公有静态成员函数,获取对象个数
cout << "t3.getValue() = " << t3.getValue() << endl; //通过对象名调用静态成员函数获取对象个数
system("pause");
}
// 结果为3
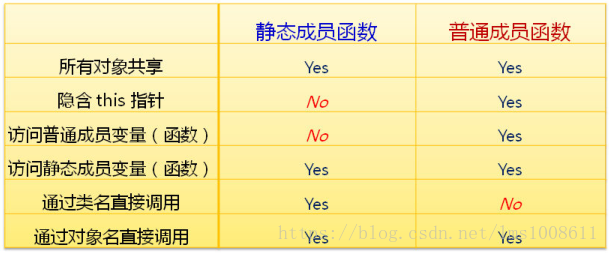
| 静态成员函数 | 普通成员函数 | |
|---|---|---|
| 所有对象共享 | yes | yes |
隐含this指针 | no | yes |
| 访问普通成员变量(函数) | no | yes |
| 访问静态成员变量(函数) | yes | yes |
上次更新: 2022/11/24, 22:50:32